Private Blockchain and Public Blockchain are both equally real, but individuals vary considerably.
Public and Private Blockchains’ Similarities:

The following are the number of common classifications of blockchains:
- Both are peer-to-peer (P2P) networks, which means that each participant has a copy of the detailed accounting system associated with digitally signed transactions.
- All use the consensus protocol to keep simultaneous copies.
- Alike public and private blockchains guarantee that the ledger cannot be altered, even if some participants fail.
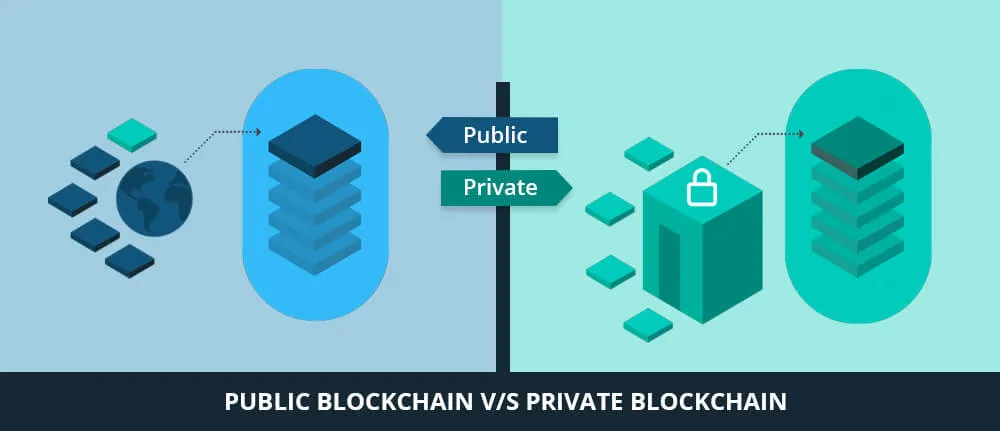
Public vs Private Blockchains- The Differences:
- Public blockchain:
Today, Public Blockchains account for the vast majority of distributed ledgers. Users named public since anyone can see the purchases occurring and join the blockchain through accessing the necessary software.
Public blockchains are also commonly referred to as permissionless. No firewall can prevent you from active participation, and anyone can use the consensus algorithm (by mining or staking).

Permissionless blockchains have been predicted to withstand censorship better than private (or semi-private) blockchains. Since anyone can connect to the network, specific mechanisms must be included in the procedure to block malicious performers from attacking anonymously.
A security-oriented approach to public chains, on the other hand, frequently comes at the expense of performance. Many blockchains suffer from scalability issues and poor performance.
Furthermore, changing a network without plunking down it can be challenging even though rarely do all participants agree on the proposed changes.
- Private blockchain:
Private blockchains, in contrast to public blockchains, have rules governing who can participate and write data to the chain (a permission environment).

They have distributed networks with a clear control hierarchy in which many nodes keep a copy of the system on the computer.

Private chains are appropriate for enterprise settings where an organization stands to profit from the assets of blockchain while still being sufficient to shield their network from outsiders.

Based on the security model, the Proof of Work (PoW) requirement is redundant, but it is also considered necessary for an open environment. Even so, in a private blockchain, PoW cannot prevent too dangerous threats since each participant’s identity is revealed and management is direct.

A more efficient algorithm, in this case, is one with specified validators, in which nodes are chosen to perform specific functions to validate transactions.
In summary, nodes must log out on each block to accomplish this. If endpoints start engaging in malicious behavior, they can be quickly captured and disconnected from the system.
- Private Blockchain and Public Blockchain Differences Summary:
The table below summarizes some of the key distinctions between these blockchain types.
| Types of Blockchains | ||
| Public | Private | |
| Data rights modification | Yes | No |
| Blockchain data reading permission | Anyone | Only invited users |
| Blockchain data writing permission | Anyone | Approved participants |
| Possession | Nobody | A single organization |
| Will the identity of the participant be revealbe? | No | Yes |
| Transaction speed | Slow | Fast |
The most significant distinction between them is: If the private investment costs to design, generate, and maintain the Blockchain, the public Blockchain will not. Simply join the pull system, and all of your Blockchain data will be made available to the community.
Which One Is The Best?
Although well-designed Public chains are more resistant to censorship, this has an impact on speed and throughput. This type of blockchain is best suited to ensuring the security of transaction execution (or smart contracts).
The private chain can prioritize system speed since it does not have to be concerned about the unique points of failure found in public blockchains. They are ideal in situations where an individual or organization must maintain control while keeping information private.
Public and private blockchains, in unique, are not mutually exclusive and are distinct technologies. Differences between public and private blockchain classifications result in multiple experiences. SmartOSC hopes that by reading the above article, businesses, and blockchain programmers will be able to better understand and identify the correct kinds of blockchain.
Contact us if you have any queries about Blockchain development services, dApps development, NFT marketplace development, Crypto wallet development, Smart contracts development.