To ensure that blockchains such as Bitcoin or Ethereum function correctly, they must be built on a complete and efficient foundation: layer 0. They range from a simple network of miners to inter-blockchain communication. This blog will help you understand the layer 0 blockchain examples.
1. What is a layer 0 blockchain?

Layer 0, the foundation of blockchain technology, is a collection of components that enable a decentralized network to function correctly. The first decentralized networks, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, appeared as simple blockchains at the beginning of the blockchain. As a result, despite its existence, the concept of layer 0 was rarely mentioned, either due to a lack of interest or a lack of solutions.
From 2020, the proliferation of blockchains, the exponential adoption of decentralized finance (Defi) applications, and the meteoric rise of non-fungible tokens (NFT) will cause scalability and interoperability issues. As a result, the concept of a layered blockchain is resurfacing. With this renaissance comes the emergence of advanced solutions that begin to populate the various levels of blockchains, including level 0.
2. Some examples of Layer 0 blockchain
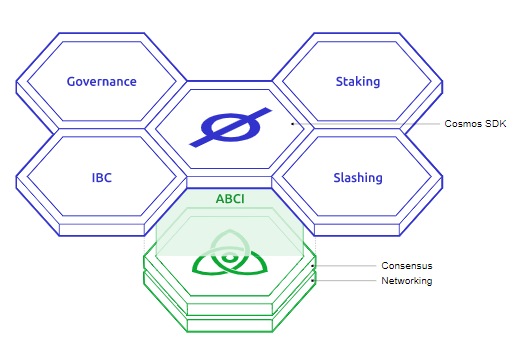
Cosmos
The Cosmos development team is responsible for the most valuable layer 0 on the market, worth nearly $150 billion. Above all, this promotes modularity and interoperability. Cosmos is a triptych of solutions born from the collaboration of its two most significant contributors, Ignite and the Interchain Foundation.
Cosmos uses these three components to present itself as the “Internet of Blockchains.” Its widespread adoption, partly because of its modularity policy, allows each blockchain to control its security.
Polkadot
Unlike Cosmos, Polkadot prioritizes security over modularity. Despite their opposing visions, there are similarities, particularly in the structure of their solution.
There is a development kit, “Substrate,” and a communication solution, “Cross-chain Message Passing,” similar to Cosmos (XCMP). However, the security of a parent blockchain, known as the “Relay chain,” is required for each blockchain (or para chain) in the network.
Layer 0 of Polkadot is much more restrictive. Nonetheless, it enables smaller blockchains to benefit from a foundation that includes an easy-to-use development kit, an intercommunication system, and a security guarantee provided by DOT, the market’s tenth most valuable cryptocurrency.
Avalanche
Avalanche’s layer 0 solution is unique in its approach to security and expansion. Unlike Cosmos and Polkadot, its architecture is waterfall-based, with a layer 1 blockchain, known as the primary network, overseeing everything. It also gives rise to three blockchains with distinct applications. For example, the “platform chain” enables the creation of new specialized blockchains known as “subnets.” All of these blockchains are built with Avalanche layer 0.
This layer 0 is far more permissive than Cosmos or Polkadot’s. Although certain parameters must be followed to ensure blockchain compatibility, developers still have options when it comes to customization. Custom chains, for example, must use the “Snowman” consensus method, but they can use their validators or the main chain. On this specific security point, developers must choose between the Cosmos and Polkadot methods.
Arweave
Arweave is a distinct and distinct solution from the first three. This proof-of-work blockchain was not designed to become a layer 0 protocol. Arweave, like Filecoin, is a blockchain that enables decentralized information storage. However, the nature of the storage distinguishes this solution from its counterpart. Indeed, everything stored on Arweave is permanent and can only be deleted with the agreement of the majority of minors on the network.
This made Arweave the ideal candidate for preserving the entire history of a significant blockchain. Solana, with its 4 petabytes (4,000,000 GB) of data generated per year when the blockchain is fully operational, is an ideal candidate. It’s difficult to believe that validators alone can ensure long-term decentralization.
As a result, the SOLAR bridge, which allows Solana transactions to be permanently stored on Arweave, began development in 2020. Transactions can be stored on a decentralized network a few minutes after they are validated using this technology. Arweave can now be a part of Solana’s layer 0, thanks to this solution.
Conclusion
Layer 0 blockchain examples, the proper foundation of blockchain technology, have only recently gained attention. However, the race for scalability and interoperability saw the layered blockchain architecture reborn in the 2020s and 2021s. Interoperability necessitates a closer relationship between existing networks. Contact SmartOSC if you need a blockchain development service for industries.
Contact us if you have any queries about Blockchain development services, dApps development, NFT marketplace development, Crypto wallet development, Smart contracts development.