Most aspects of our professional and personal lives are governed by contracts and are necessary for modern society to function.
As an introduction to Blockchain technology, Smart Contracts play a critical role in making transactions safer and more secure and functioning in an organized manner. Not only that, but it makes other components, such as applications running on these platforms, more accessible. But what exactly is a smart contract? This is a novice’s guide to smart contracts with a real-life example.
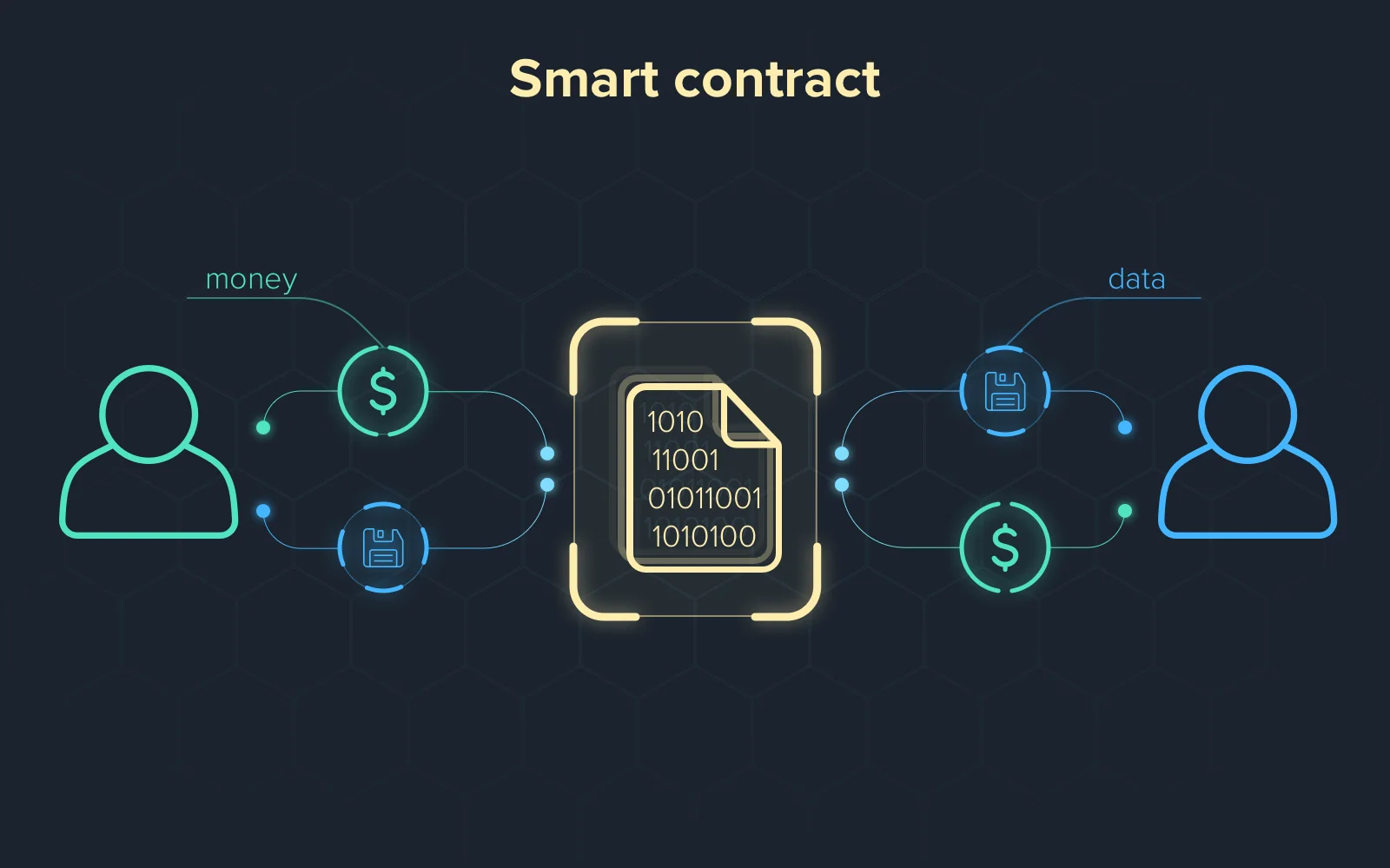
A smart contract is a self-executing contract in which the terms of the buyer-seller agreement are directly written into lines of code. The code and the agreements are distributed across a decentralized blockchain network. Transactions are irreversible and trackable; the code controls the execution.
Smart contracts enable trusted agreements and transactions to be carried out between disparate, anonymous parties without the use of a central authority, legal system, or external enforcement mechanism.
While blockchain technology has become known primarily as the foundation for bitcoin, it has developed far beyond that role.
The various value advantages of smart contracts present a promising case for their use in different real-world use cases. This list of some of the most notable blockchain smart contract examples available today.
Smart contracts have the potential to reduce costly errors. The ability of these contracts to automate workflows and sharpen calculations also aids in the reduction of work hours.
Santander InnoVentures reported on the advantages and opportunities associated with using blockchain in finance. Smart contracts will enable fundamental changes in the infrastructure and processes of the financial services industry. Distributed ledgers, they believe, will become the preferred choice for managing large volumes of transactions. In 2022, these savings are expected to total $15-20 billion per year.
In this industry, smart contracts are used to record property ownership of any structure. Eliminating the need for lawyers or brokers improves transaction speed and efficiency. Sellers can direct the process.
According to blockchain thought leader Rob Massey, smart contracts enable a more transparent and cost-effective alternative to property title management. Title defects can obstruct transfers, resulting in legal fees. On the other hand, smart contracts record the history of a property, location, and all further essential details required for title assessment. They aid in the prevention of fraud by employing tamper-proof and secure encrypted codes.
More healthcare institutions are using blockchain to provide dependable automation and up-to-date security measures. Hospitals are popular targets for cybercriminals because they contain a wealth of sensitive data. Even industry titans like UCLA Health have been victims of data breaches, with 4.5 million patient records compromised.
In this environment, ensuring secure patient data sharing across healthcare providers is critical to maintaining care standards. Smart contracts enable the safe storage of patient data on a blockchain, which it can only access with the patient’s private key. Patients can ensure that their medical providers have constant access to the information they require and that their data is secure.
Blockchain voting systems could be the way elections are conducted in the future. Blockchain voting systems could increase accessibility, encourage greater voter participation, and speed up tallying and reporting votes by making voting safe and convenient through digital means. Smart contracts could validate voters’ identities to prevent multiple votes from being cast, a common goal of election hackers.
Every year, millions of dollars are spent in the insurance industry on claim processing. Money is lost because of fraudulent claims. Smart contracts improve claim processing by performing frequent error checks and help administer policies from individuals or organizations. Consumers will benefit from lower costs, including premium rates, as processing times are reduced.
According to Lloyd’s of London, insurance companies will fill in the gaps in coverage caused by the underwriting process because they will better manage risks from corporate buyers.
Blockchain is the underlying technology that allows expanding smart contacts. I hope you enjoyed this tutorial on what a smart contract is. If you need or want advice on blockchain development services, don’t hesitate to contact SmartOSC.
Increased acceptance and knowledge sharing have aided the spontaneous growth of cryptocurrency over the last…
Blockchain can be intimidating to research, but attending cryptocurrency events is one of the best…
Blockchain has made inroads into all major industries and is also becoming a part of…
In recent years, blockchain lending solutions have grown in popularity as a way to earn…
The scalability trilemma is still one of the blockchain's most pressing issues. Here are some…
Many people are looking for ways to get involved in the crypto world as the…